Describe How Schwann Cells Form the Myelin Sheath
Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma encasing the nerve processes. It is interrupted at the nodes of Ranvier.
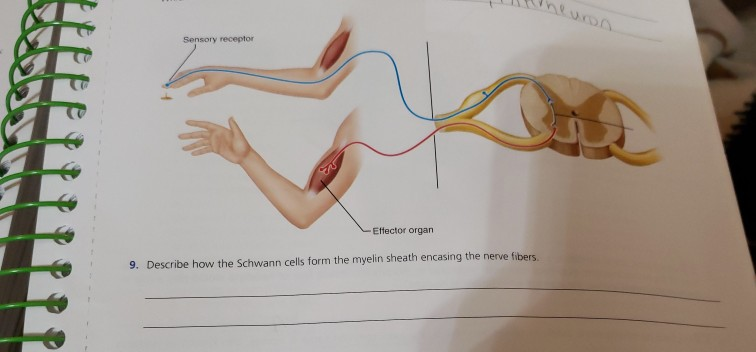
Solved Sensory Receptor Effector Organ 9 Describe How The Chegg Com
It is formed by a single extension of the nerve cell cytoplasm.
. Describe how schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurolemma encasing the nerve processes. Kindly login to access the content at no cost. These are both what are packed around the axon to form the myelin sheath from the cell.
Myelin-shaped when Schwann cells fold themselves over the axon again and again framing layers of film Neurilemma-pushes the Schwann cells cytoplasm and organelles edge of the cell. The myelin sheath is formed by myelinating Schwann cells wrapping across the axons of sensory and motor neurons. The Schwann cells wrap themselves tightly around the axon like a.
The sheath it packed tightly in spiral casings around the axon. Neurilemma is the collective term used for cytoplasm and nuclei present around the myelin sheath which helps in the regeneration process of nerves. Lab 8 nervous system.
Each Schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon. Site of the nucleus and most important metabolic area. Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma encasing the nerve processes.
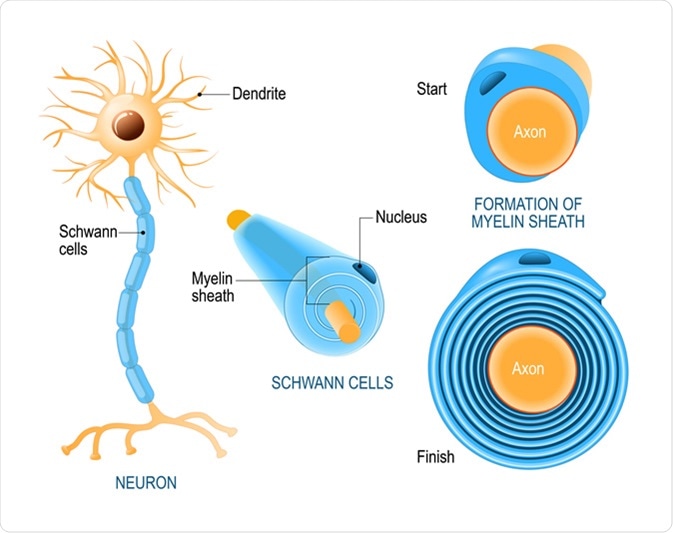
Schwann cells are individualized as single myelin sheath to form the axon. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma. Myelin sheath is formed by consecutive wrappings of Schwann cell membrane around the axon of a neuron.
It then begins to rotate around the axon wrapping it loosely. This E-mail is already registered as a Premium Member with us. It then begins to rotate around the axon wrapping it loosley in successive layers of its plasma membrane.
Myelin is formed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system PNS and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system CNS. Who are the experts. Also each Schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon whereas oligodendrocytes form myelin sheaths for multiple surrounding axons.
Schwann cells or neurilemma cells are the cells which form the myelin sheath around neuronal axons in the peripheral nervous system PNS only. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the399686. Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing the nerve fibers.
Schwann Cells vs Oligodendrocytes. Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma encasing an axon. Insulates the nerve fibers.
Schwann cells or neurilemma cells are the cells which form the myelin sheath around neuronal axons in the peripheral nervous system PNS only. The Schwann cells wrap themselves tightly around the axon like a jellyroll. See the answer See the answer done loading.
By signing up youll get thousands of. Schwann cells are another name for neurilemma cells. Histology of Nervous Tissue.
Experts are tested by Chegg as specialists in their subject area. It is a laminated sheath made up of lipoproteins. Throughout the downstream portion of the human dystrophin gene the Schwann cell promoter is found which results in shortened transcripts that are synthesised in a tissue-specific fashion.
Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma. 4 rows Schwann cells also known as neurolemmocytes are flat cells which make up myelin sheaths on. Axons are wrapped in special cells called Schwann cells for the effective and speedy action of signal transmission.
Schwann cells form a sheath around the axon which is known as the myelin sheath. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma. Schwann cells are located around the axon and there are small gaps between each cell.
In case of peripheral nerves the myelin sheath is formed by the Schwann cells and in the central nervous system the. However whilst Schwann cells myelinate axons of the PNS the oligodendrocytes provide myelination to axons in the central nervous system CNS. A Schwann cell becomes apposed to an axon and envelopes it in a trough.
Myelin itself forms by the spiral wrapping around an axon of an enormously expanded glial plasma membrane that then compacts. Axons in the peripheral nervous system are myelinated by special supporting cells called Schwann cells which wrap themselves tightly around the Axon in Jelly roll fashion so that when the process is completed a tight core of plasma membrane material called the myelin. Wrap themselves tightly around the axon in jelly roll fashion.
Each Schwann cell forms a single myelin sheath around an axon. Describe how the Schwann cells form the myelin sheath encasing the nerve fibers. It becomes supposed to an axon and envelopes it in a trough.
A Schwann cell surrounds the axon invaginate it and the. Myelin is formed by Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system PNS and oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system CNS. We review their content and use your feedback to keep the quality high.
In contrast each oligodendrocyte forms multiple sheaths up to 30 or more around different axons Figure 1. Describe how Schwann cells form the myelin sheath and the neurilemma. Its outer surface is encased in neurilemmal sheath.
Neurilemma is the collective term used for cytoplasm and nuclei present around the myelin sheath which helps in the regeneration process of nerves.
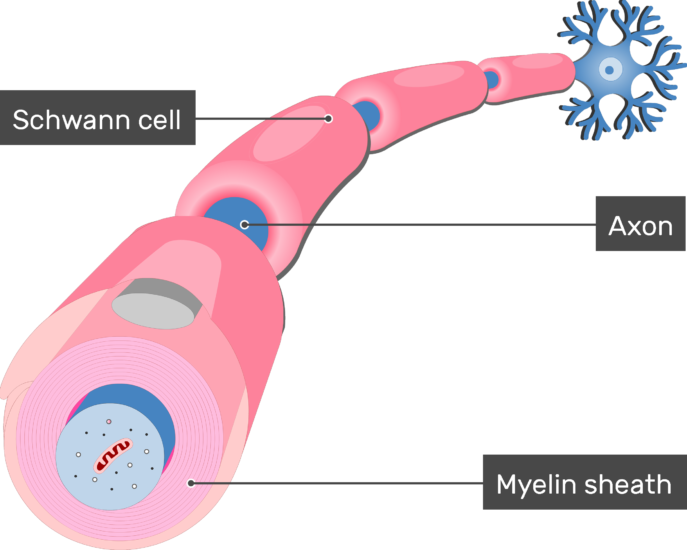
Myelination Of Axons By Schwann Cells

Solved Sanary Oper Id 9 Describe How The Schwann Cells Chegg Com
Comments
Post a Comment